


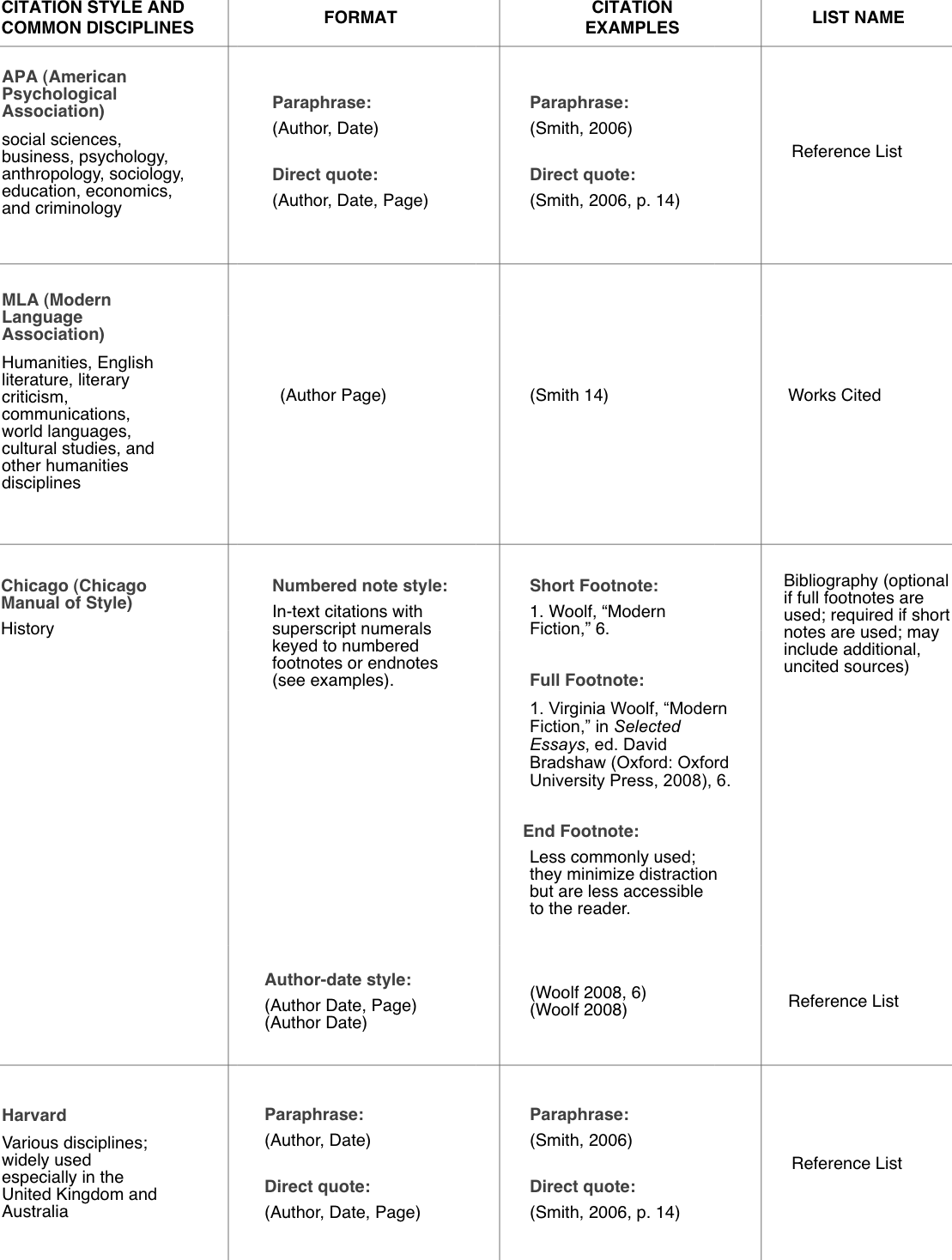
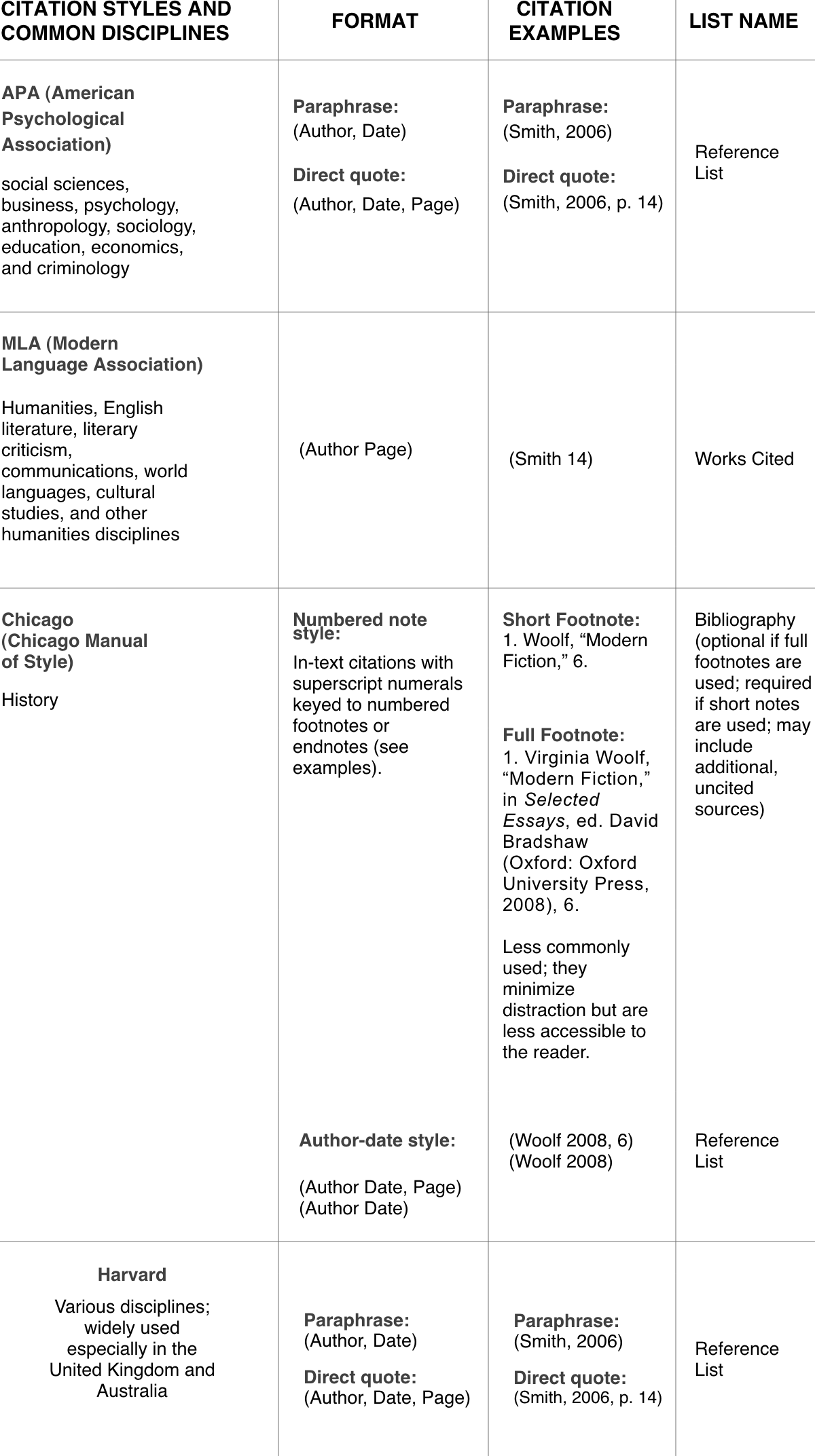
Citation Style and Common Disciplines | Format | Citation Examples | List Name |
|---|---|---|---|
APA (American Psychological Association) social sciences, business, psychology, anthropology, sociology, education, economics, and criminology | Paraphrase: (Author, Date) Direct quote:(Author, Date, Page) | Paraphrase: (Smith, 2006) Direct quote:(Smith, 2006, p. 14) | Reference List |
MLA (Modern Language Association) humanities, English literature, literary criticism, communications, world languages, cultural studies, and other humanities disciplines | (Author Page) | (Smith 14) | Works Cited |
Chicago (Chicago Manual of Style) history | Numbered note style:
In-text citations with superscript numerals keyed to numbered footnotes or endnotes (see examples).
| Short Footnote: 1. Woolf, “Modern Fiction,” 6. Full Footnote: 1. Virginia Woolf, “Modern Fiction,” in Selected Essays, ed. David Bradshaw (Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2008), 6. Endnote: Less commonly used; they minimize distraction but are less accessible to the reader. | Bibliography (optional if full footnotes are used; required if short notes are used; may include additional, uncited sources) |
Author-date style:
(Author Date, Page)
(Author Date)
| (Woolf 2008, 6) (Woolf 2008) | Reference List | |
Harvard various disciplines; widely used especially in the United Kingdom and Australia | Paraphrase: (Author, Date) Direct quote:(Author, Date, Page) | Paraphrase: (Smith, 2006) Direct quote:(Smith, 2006, p. 14) | Reference List |




Level-up current events into dynamic learning!